interpretation of triaxial compression test results|triaxial test calculations : consultant Soil triaxial testing is a fundamental procedure in geotechnical engineering, used to determine a sample’s shear strength parameters. During triaxial testing, a cylindrical soil sample is enclosed in a rubber membrane and placed within a .
webXehli G Pelada Deitada na Cama – Nua Grátis. Xehli G Youtuber novinha do telegram pelada, gostosa nua na cama antes de dormir, mostrou a marquinha de biquíni no seu .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webDownload SiriusXM 5.5.7 APK - SiriusXM is an application that provides users with access to all of the radio stations from Sirius XM network. 25% OFF 1Password Families • 5 .
First, an experimental study of the unconsolidated-undrained (UU) triaxial compression test with different moisture contents (w = 10%, 20% and 34%) and confining pressures (σ3 = σc = 0.05.The triaxial shear test is the most versatile of all of the methods for testing the shear strength of soil and finding its cohesion (c) and angle of internal friction (φ). It can measure the total, as .This paper provides an introduction to the triaxial test, explaining why the test is performed, the stress state of a tested soil, required test system components, and the general procedure for .describes the general procedures used to perform a triaxial test and the specific procedures used for the drained test. Following the description of these procedures is a discussion of the .

Introduction - Purpose. This presentation describes the triaxial test and related equipment. The following geotechnical problems illustrate the application of the triaxial test. Earth dams are .Soil triaxial testing is a fundamental procedure in geotechnical engineering, used to determine a sample’s shear strength parameters. During triaxial testing, a cylindrical soil sample is enclosed in a rubber membrane and placed within a .triaxial tests, either directly or by interpretation through some theory. The mechanical properties most often sought from triaxial tests are stress–strain relations, vol ume change or .1 2016. Contents. Preface About the Author. Principles of Triaxial Testing. 1.1 Purpose of triaxial tests. 1.2 Concept of testing. 1.3 The triaxial test. 1.4 Advantages and limitations. 1.5 Test .
The paper introduced several new types of triaxial instruments and test techniques developed in response to the problems, and prospects have been made for further study of triaxial tests, . Consolidated-undrained triaxial compression tests with pore-pressure measurements are particularly useful and common, because the test results allow for interpretation of both drained and undrained strength parameters. Triaxial test is approved to be the most suitable method for studying the mechanical properties of rocks and soils in lab. Through conventional triaxial tests, parameters like the strength of rocks and soils can be obtained, thus providing guidance for the design and construction of geotechnical engineering. With the development of geotechnical engineering, . The triaxial test can also be used to determine other variables such as the shear stiffness G, and permeability k. Triaxial Test Types. There are three fundamental triaxial tests that can be conducted in the laboratory, each .
triaxial test protocol
Apparatus for Triaxial Compression Test: The main apparatus for triaxial compression test is the triaxial cell that is shown in Fig. 13.19 with all its accessories. The triaxial cell is a high-pressure cylindrical cell made of Perspex or other transparent material fitted between the base and the top cap.
The results show that triaxial data requires mi values outside (mi >50) the typically assumed range (mi ≤50). These high mi values appear to be needed to fit data at high confining stress levels .index, unconfined compression, triaxial compression, Brazilian test, and direct shear. The uniaxial (or unconfined) compression test provides the general reference value, having a respective analogy with standard tests on concrete cylinders . The uniaxial compressive strength (q u = F u) is obtained by compressing
Therefore, the results obtained by conventional triaxial tests cannot completely reflect the real conditions. Compared with conventional triaxial tests, true triaxial tests can realize independent control of three-dimensional stress and the test results are much closer to the real conditions. True triaxial apparatus was first developed by KjellmanResults. A typical stress-strain diagram deriving from a Uniaxial Compression Test of an undisturbed specimen of basalt is presented in Figure 1. The UCS is the peak value of the diagram and is equal to 44.7 MPa. Photos of the specimen before and after the test are presented in Figure 2.CONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED TRIAXIAL COMPRESSION TEST FOR UNDISTURBED SOILS TXDOT DESIGNATION: TEX-131-E CONSTRUCTION DIVISION 5 – 10 LAST REVIEWED: SEPTEMBER 2014 4.9 Obtain an initial buret reading and then open appropriate drainage valves so specimen may drain from both ends into the buret. 4.9.1 At increasing intervals of elapsed . A total of four multistage triaxial compression tests were conducted over the range of confining pressures of 1–15 MPa as shown in Table 1.From the results of triaxial compression test, the stress–strain curve was plotted to maximum peak loads against corresponding values of confining pressure to build the complete Mohr–Coulomb failure .
triaxial test for shear strength
Drained triaxial compression tests on sand are common in geotechnical engineering due to their application in determining strength and critical state properties, and calibration of constitutive models. However, questions around reliability of test results due to strain localization and specimen non-uniformity have sparked debate around the adequacy of .
Students and practicioners of soil mechanics alike are used to seeing triaxial test results that look like this (from DM 7.01): Ideally, the Mohr-Coulomb failure line should be straight, but with real soils it doesn't have to be that way. With the advent of finite element analysis we also have the failure function to consider,.Results and Parameters derived from the Oedometer Test. The following soil properties are derived from the Oedometer Test: The Pre-consolidation Pressure: The maximum effective stress that the soil specimen has sustained in its geological history. The Compression Index C C: C C is an index associated with the compressibility of the soil. In .
refractometer emulsion
For these soil types, ASTM D2850, unconsolidated, undrained triaxial compression, is a more suitable test method for strength determination and will generally result in higher shear strength. . Avoiding moisture loss and sample disturbance is key to producing valid test results throughout the sample preparation process. Consolidated – Drained Triaxial Test. The consolidated drained triaxial compression test is conducted in the same manner as the consolidated undrained test, with the exception that during shear, the back pressure is still .
View Interpretation of Triaxial Test Results.pdf from CE 383 at Purdue University. CE 383 - Geotechnical Engineering I Learning Objectives INTERPRETATION OF TRIAXIAL TEST RESULTS Understand response .First publication of its kind in 25 years, this 900-page volume serves as an engineer’s guide for triaxial testing. Subjects include: equipment, test methods, and test interpretation and errors, and new test varieties.test data, interpret its mechanical properties and apply these to a range of common geotechnical design problems at ultimate and serviceability limiting states. Triaxial Testing of Soils Poul V. Lade,2016-05-02 Triaxial Testing of Soils explains how to carry out triaxial tests to demonstrate the effects of soil behaviour on engineering designs.
iv Special thanks to the funding bodies for this research: Klohn Crippen Berger, Lassonde Institute of Mining, University of Toronto, and Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Drained triaxial compression tests on sand are common in geotechnical engineering due to their application in determining strength and critical state properties, and calibration of constitutive . He again confirmed his finding from the experimental test results from solid cylindrical specimens of feldspathic Darley Dale sandstone tested under CTC and RTE test conditions [17]. . Takahashi, T. Narita, Y. Tomishima, R. Arai, Various loading systems for rock true triaxial compression test (in Japanese), J. Japan Soc. Eng. Geol. 42 (2001 .
triaxial test calculations pdf
The procedure for performing and interpreting multistage triaxial compression tests is described. The results obtained from unconsolidated undrained and isotropically con-solidated undrained tests on normally consolidated alluvial clay and overconsolidated colluvial .the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard. 2. DEFINITIONS 2.1 Triaxial Compression Test—the triaxial compression test a test in which a cylindrical specimen of soil or rock encased in an impervious membrane is subjected to a confining pressure and then loaded axially to failure in compression.
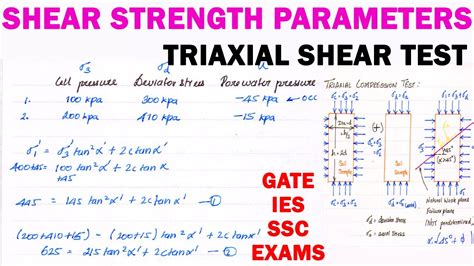
To summarise for a triaxial compression test: σ 1 – Vertical (axial) Stress (think of this as the vertical load applied to the sample). This also known as the Major Principle Stress. Can also be call σ v. σ 3 – Confining Pressure (think of this as cell pressure). This is also known as the Minor Principle StressI have looked at whole text books on triaxial tests, which talk about alot of stuff to help clarify a bit, but I am still not fully clear what to look for in these graphs. Attaching some of the graphs for reference, but I have at least 100 test results so looking for a more general understanding on this rather than this specific test.loadings used in a cyclic triaxial test to approximate a range of dynamic loading situations. Note the division between static and dynamic frequencies is generally considered to be in the order of 0.05 - 0.1 Hz (Ishihara, 1996). Table 1 – Typical test frequency ranges for cyclic triaxial testing. Loading type Typical test frequency8. Rate of axial compression shall be selected such that failure is produced within a period of approximately 5 to 15 minutes and readings of the load and compression measuring gauges be taken. 9. The test shall be continued until the maximum value of the stress has been passed or until an axial strain of 20 percent has been reached. 10.
triaxial test calculations
triaxial soil chart
triaxial shear test is code
Resultado da (Supports wildcard *) . Tags. Copyright? +-brandy & mr whiskers 915 ? +-brandy and mr. whiskers 299 ? +-disney 159979 ? +-e621 490 ? +-plants .
interpretation of triaxial compression test results|triaxial test calculations